How to Write Effective Prompt Instructions: A Conversational Guide for Better AI Results
AI tools are everywhere today — from chatbots that answer customer questions to sophisticated models that generate code, copy, and creative work. But the quality of AI output depends more on the prompt than the model. Good prompt instructions bridge human intent and machine understanding. In this article you’ll learn practical, research-backed techniques for writing clear, efficient, and reliable prompts. Whether you’re a marketer, developer, product manager, educator, or curious user, you’ll walk away with concrete templates, step-by-step strategies, and real-world examples that improve accuracy, reduce iteration time, and unlock the full potential of generative AI.
Why Prompt Instructions Matter
Think of a prompt as the brief you give a collaborator. Vague or ambiguous briefs produce inconsistent results, while clear briefs shorten the feedback loop and improve quality. With AI, this dynamic is amplified: the model has no world context beyond the text you provide, so specificity and structure matter.
- Efficiency: Better prompts reduce back-and-forth and save human time.
- Accuracy: Structured prompts steer the model toward the right format and content.
- Controllability: You can guide tone, style, and constraints to match use cases.
- Reproducibility: Well-documented prompts produce reliable outputs across runs.
- Task: Clear statement of the objective. (What do you want?)
- Output format: Define structure, sections, and length. (How should it look?)
- Audience: Who is this for and what do they know?
- Tone & style: Voice, formality, and examples.
- Context & constraints: Necessary background, facts, exclusion rules.
- Examples: Desired and undesired outputs.
- Validation rules: Checks the model should run on its output (e.g., list 5 items, include citations).
- Ask for explanation: Optionally request a brief rationale or steps taken.
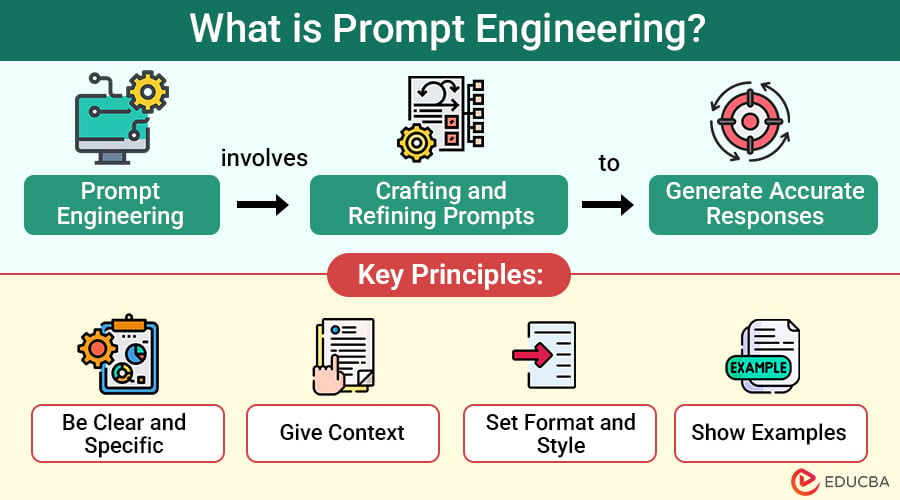
Core Principles of Effective Prompt Instructions
Before diving into templates and examples, keep these guiding principles front of mind.
1. Be Specific and Concrete
Replace vague requests with explicit instructions. Instead of “Write a marketing email,” say “Write a 150–200 word marketing email for a productivity app targeting remote teams, featuring a 20% discount code and a friendly, professional tone.”
2. Define Output Structure
Tell the model exactly how you want the response formatted: headings, lists, length, sections, or even JSON. Structured outputs are easier to parse and validate.
3. Provide Context and Constraints
Context can include audience, use case, brand voice, examples, or relevant facts. Constraints limit the output—word counts, prohibited terms, or required elements.
4. Use Examples and Counter-Examples
Show the model a good example and a bad one. Examples teach style, content density, and formatting nuances more effectively than abstract rules.
5. Ask for Step-by-Step Reasoning When Needed
For complex tasks (e.g., coding, multi-step problem solving), ask the model to outline its approach before producing the final output. This improves traceability and gives you an opportunity to correct course early.
6. Iterate with Short Tests
Start with a concise prompt that includes the essentials, run quick tests, then expand details based on observed model behavior. Small adjustments often yield big improvements.
Prompt Anatomy: A Practical Template
Use this template as a starting point. It balances clarity with flexibility and can be adapted across tasks.
Example prompt using the template:
Task: Create a landing page headline, 3-sentence subheading, and 5 bullet benefits for a new AI note-taking app. Output format: JSON with keys: headline, subheading, benefits (array). Audience: Busy knowledge workers aged 25–45 who use multiple devices. Tone & style: Concise, professional, slightly playful. Context & constraints: Include “syncs across devices.” Keep headline < 10 words. No technical jargon. Examples: Good: "Capture ideas, anywhere." Bad: "An application for asynchronous note capture and cross-device persistence." Validation: Return JSON only. Benefits must be 6–12 words each.
Specific Prompt Patterns and Use Cases
1. Content Writing (Blog Posts, Landing Pages)
Prompts should include word count, audience, tone, SEO keywords, and structure. For blog posts, provide target keywords and a desired outline or ask the model to suggest one.
Template:
Write a [word count] blog post for [audience] about [topic]. Include these keywords: [keywords]. Use H2 and H3 headings with short paragraphs. Provide examples, a 3-bullet checklist, and a conclusion with a call to action.
Tip: To improve SEO, ask for internal link anchor suggestions and meta description variations (150–160 characters).
2. Code Generation and Debugging
For coding tasks, include the language, environment, expected input/output, libraries allowed, and example test cases. If debugging, include code, error message, and desired behavior.
Template:
Task: Write [language] function that [does X]. Constraints: Use [libraries], follow [style guide], time complexity Output pairs. Tests: Provide unit tests in [framework].
3. Data Analysis and Spreadsheets
Include sample data, goal (e.g., pivot table, chart), and preferred tools (Excel, Google Sheets, Python). Ask for step-by-step instructions and formulas or code.
Template:
I have a dataset with columns A, B, C. Create a pivot table to show [metric] by [category]. Provide Excel formulas or Python pandas code and a short explanation of each step.
4. Customer Support and Conversational Agents
Provide user personas, common issues, allowed responses, and escalation rules. Include tone guidelines and regulatory constraints where applicable.
Template:
Persona: [persona description]. User intent examples: [list]. Do not offer legal/medical advice; escalate to human if [conditions]. Give 3 response variants: concise, empathetic, and proactive.
Advanced Techniques to Improve Reliability
1. Chain-of-Thought and Decomposition
Ask the model to break tasks into steps and produce intermediate outputs. This reduces hallucinations for complex reasoning and makes errors easier to spot.
2. Few-Shot Prompting
Include 2–5 high-quality examples demonstrating the desired input-output mapping. Few-shot prompting helps align the model’s output distribution to your needs.
3. Role Prompting
Start the prompt by assigning a role, such as “You are a senior UX researcher” or “You are a legal analyst.” This frames the model’s perspective and style.
4. Temperature and Sampling Control
When the system allows, set temperature low (0–0.3) for deterministic outputs and higher (0.7–1.0) for creative exploration. For precise tasks like code or legal text, keep temperature near 0.
5. Use Constraints as Guards
Explicitly ban certain behaviors or phrases to avoid unwanted directions, and require the model to check for them before finalizing the output.
Practical Examples and Templates
Here are ready-to-use prompts for common tasks. Each is compact and designed to be copy-pasted into most chat-based AI interfaces.
Blog Post Outline + Draft (SEO Focused)
You are an expert content marketer. Create a detailed outline for a 1,500-word blog post on "[primary keyword]". Include H2 and H3 headings, suggested word counts per section, and 5 target long-tail keywords. Then draft the introduction (150–200 words) and a 100-word conclusion with a CTA.
Product Description for eCommerce
Write a 150-word product description for [product name]. Audience: [audience]. Tone: friendly, conversion-focused. Include 3 bullet-point features and 2 social-proof lines (short testimonials). End with a 6-word call to action.
Customer Support Reply Variants
You’re a helpful support agent for [company]. The customer reports: [issue]. Provide three responses: 1) immediate empathetic reply, 2) technical troubleshooting steps, 3) escalation template to send to engineering. Keep each under 80 words.
Testing and Evaluation Checklist
Before using a prompt in production, run this checklist to ensure reliability and safety.
- Does the output meet length and format requirements?
- Is the tone consistent with brand guidelines?
- Are facts and numbers accurate? (Validate against sources)
- Does it avoid disallowed content or biased language?
- Are required elements (CTAs, keywords, legal disclaimers) present?
- Is the output stable across multiple runs?
Automate tests where possible: run prompts with varied inputs and compare key metrics (e.g., keyword presence, JSON validity, required fields).
Common Mistakes and How to Fix Them
Mistake: Overly Long or Ambiguous Prompts
Problem: The model ignores core requirements or contradicts itself.
Fix: Simplify and separate requirements into labeled sections (Task, Format, Constraints). Use bullet points and short sentences.
Mistake: Missing Validation Rules
Problem: Output lacks required elements or violates constraints.
Fix: Add explicit validation steps and ask the model to self-check before returning the final output.
Mistake: No Examples Provided
Problem: Tone and style are inconsistent.
Fix: Provide 1–3 high-quality examples of desired outputs and one counter-example.
Ethics, Safety, and Bias Considerations
Prompts can influence model outputs in ways that perpetuate bias or produce harmful content. Mitigate risks by:
- Including instructions to avoid discriminatory language and to use inclusive examples.
- Adding checks to refuse requests for illegal, medical, or legal advice where your system or policy prohibits it.
- Requiring citations for factual claims or asking the model to flag uncertain statements.
- Testing prompts across diverse demographic scenarios to detect biased behavior.
Document and version-control high-impact prompts. Treat them like code: review, test, and maintain an audit trail of changes and approvals.
Operationalizing Prompt Instructions
To move from experiments to production, adopt these practices:
- Prompt Libraries: Maintain a curated repository of approved prompts with metadata (purpose, owner, last reviewed).
- Versioning: Track changes using semantic versioning and changelogs.
- Monitoring: Log outputs and user feedback; set alerts for deviations or harmful outputs.
- Human-in-the-loop: For sensitive tasks, require human review or final sign-off.
- Training: Teach teams how to craft, test, and store prompts effectively.
Internal and External Link Recommendations
Internal linking improves SEO and user navigation. Suggested internal anchors:
- Prompt engineering guide — anchor: “prompt engineering guide”
- AI prompt templates — anchor: “prompt templates”
- AI ethics and bias — anchor: “AI ethics”
High-authority external links to include (open in new window):
- OpenAI research pages — for model behavior and best practices: https://openai.com/research
- ACL Anthology or similar NLP conferences — for technical background on prompting and few-shot learning
- Harvard Berkman Klein or Stanford Human-Centered AI — for ethics guidelines and bias mitigation
SEO and Social Sharing Optimization
SEO elements to include on publishing:
- Primary keyword: prompt instructions (target density ~1–1.5%)
- Meta description examples (150–160 chars): “Learn how to write clear prompt instructions for AI with templates, examples, and practical tips to boost reliability and speed up workflows.”
- Suggested OG title and description for social: same as headline and meta description; include a strong visual.
- Tweet-ready quote: “Good prompts are the secret sauce of reliable AI — clear, specific, and testable.” (under 280 chars)
FAQ (Optimized for Voice Search and Featured Snippets)
What is a prompt instruction?
A prompt instruction is the set of textual directions you give an AI model describing the task, desired format, constraints, and context for generating output.
Why are examples important in prompts?
Examples demonstrate the desired structure and tone, reducing ambiguity and improving output consistency.
How can I prevent AI from hallucinating facts?
Ask for citations, set the model to low creativity (temperature), require the model to mark uncertain statements, and validate outputs against authoritative sources.
How do I ensure consistent tone across outputs?
Provide explicit tone guidelines, sample lines, and a short style guide within the prompt. Use role prompting to frame perspective.
Image Alt Text Suggestions
- “Person typing prompt instructions into a laptop, surrounded by notes”
- “Flowchart showing prompt structure: task, format, context, examples”
- “Side-by-side comparison of vague and precise prompts”
Schema Markup Recommendation
Use Article schema with properties:
- headline
- description
- author
- datePublished
- wordCount
- image
- keywords
Include FAQ structured data for the Q&A section to improve chances of appearing in rich results.
Conclusion
Clear prompt instructions are the foundation of effective AI use. By being specific, providing structure, including examples, and iterating with tests, you can dramatically improve AI outputs and reduce wasted time. Treat prompts as production artifacts: document them, version them, and monitor their performance. Start small with concise templates, validate outputs, and scale the ones that work. The result: faster workflows, more reliable content, and AI that behaves like a predictable teammate.
Next step: Try the “Blog Post Outline + Draft” prompt above with one of your topics and run three quick iterations at different temperatures. Keep the best output, document the prompt, and add it to your prompt library.